Nano-Misting Technology for Microclimates
The Science Behind Nano-Misting Systems
Nano-misting technology relies on ultrafine water droplets, typically between 10 to 50 microns in diameter, to create controlled microclimates. Unlike traditional misting systems, which produce larger droplets that often leave surfaces wet, nano-misting uses high-pressure pumps to atomize water into a nearly invisible fog. This fog evaporates rapidly, absorbing ambient heat and cooling the surrounding air by up to 20°F. The process mimics natural evaporative cooling but with precision, thanks to sensors that monitor temperature, humidity, and airflow. These systems can be integrated with smart controls, allowing real-time adjustments to maintain optimal conditions for specific environments.

Applications in Agriculture and Horticulture
In agriculture, nano-misting is revolutionizing crop management by providing precise hydration without overwatering. Greenhouses equipped with these systems maintain ideal humidity levels, preventing plant stress and reducing fungal growth. Vertical farms benefit from targeted misting, ensuring even water distribution across densely packed crops. The technology also supports hydroponic setups, where root systems require consistent moisture. By reducing water usage by up to 70% compared to traditional irrigation, nano-misting addresses both sustainability and cost-effectiveness. Farmers report higher yields and improved crop quality, particularly in arid regions where water scarcity limits conventional farming.
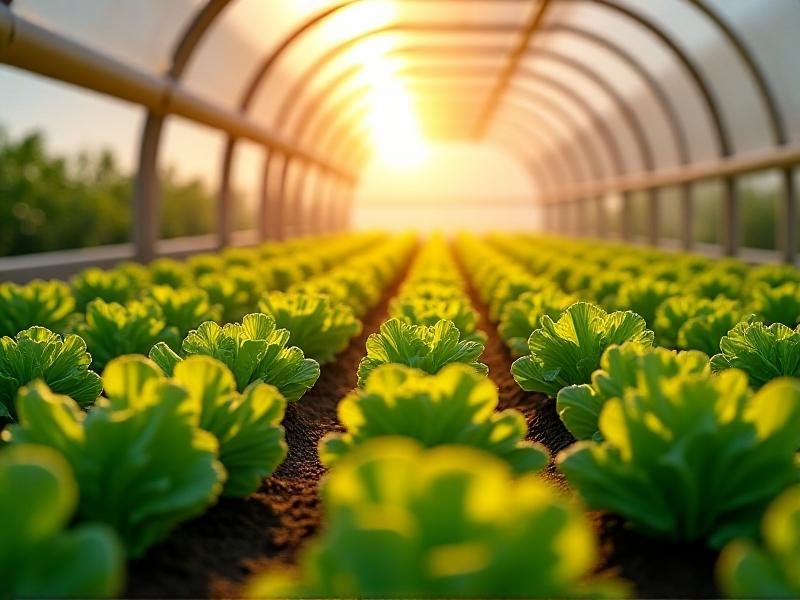

Revolutionizing Urban Spaces with Nano-Misting
Urban heat islands, exacerbated by concrete and limited greenery, are increasingly mitigated by nano-misting. Public plazas, transit hubs, and outdoor dining areas deploy misting systems to enhance comfort during heatwaves. The technology integrates seamlessly into architectural designs, such as mist-emitting pergolas or retractable awnings. Cities like Dubai and Phoenix use these systems in parks to make outdoor activities viable even in extreme temperatures. By lowering ambient temperatures locally, nano-misting reduces reliance on energy-intensive air conditioning, offering a sustainable alternative for urban cooling.
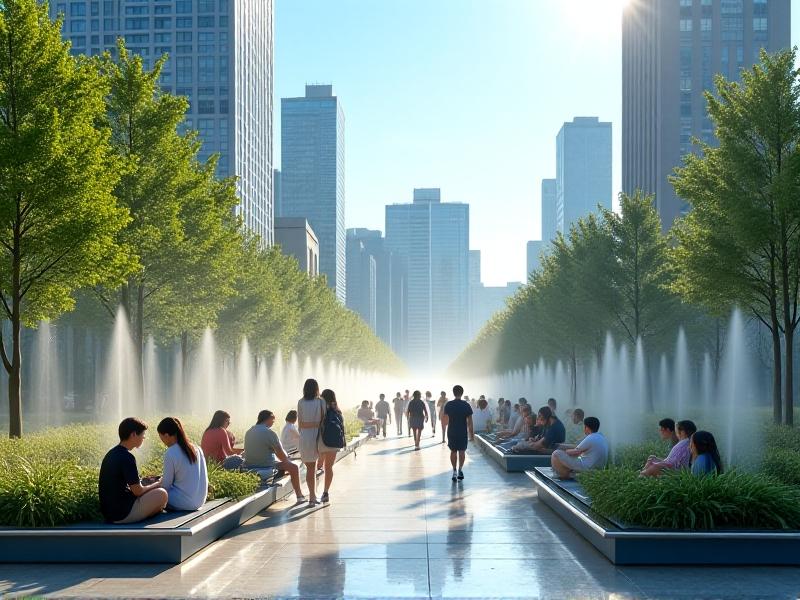

Advantages Over Traditional Climate Control
Nano-misting outperforms conventional methods in energy efficiency and adaptability. Traditional AC systems cool entire buildings, while misting targets specific zones, cutting energy use by up to 50%. Unlike swamp coolers, which add humidity to arid air, nano-misting adjusts outputs based on real-time data, avoiding excessive moisture. Its portability allows deployment in remote or temporary settings, from construction sites to event venues. Maintenance is minimal, as closed-loop systems recycle water and resist mineral buildup. Users also appreciate the silent operation and absence of chemical refrigerants, aligning with eco-friendly initiatives.

Challenges and Limitations
Despite its benefits, nano-misting faces hurdles. Initial installation costs can be high, particularly for custom-designed systems. Water quality is critical—impurities can clog nozzles, requiring filtration or softeners. In humid climates, evaporation slows, reducing cooling efficacy. Wind dispersal also poses challenges, as gusts scatter mist unevenly. Maintenance demands expertise, and repairs may require specialized parts. Additionally, public misconceptions about “getting wet” persist, though modern systems are designed to avoid visible dampness. Addressing these limitations requires tailored solutions and consumer education.
Future Innovations and Trends
Emerging trends include AI-driven systems that predict weather patterns and adjust misting schedules autonomously. Researchers are experimenting with solar-powered pumps to enhance off-grid applications. Hybrid systems combining nano-misting with shade structures or wind barriers aim to optimize microclimate control. Material science advances promise self-cleaning nozzles coated with hydrophobic surfaces. The integration of IoT enables remote monitoring via smartphones, empowering users to customize settings. As costs decline, residential adoption is expected to rise, transforming patios and gardens into year-round comfort zones.
Implementing Nano-Misting in Everyday Environments
For businesses and homeowners, adopting nano-misting starts with assessing spatial needs and climate conditions. Compact units are ideal for patios, while larger installations may require professional design. Retrofitting existing structures with misting lines is common, but new builds can incorporate hidden nozzles for aesthetics. Maintenance contracts ensure longevity, with monthly checks for nozzle clarity and pump performance. Case studies show restaurants increasing outdoor seating revenue by 40% after installing misting systems, highlighting their practical value.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nano-misting supports water conservation, using up to 90% less water than sprinklers. Closed-loop systems recycle water, minimizing waste. Solar-powered options further reduce carbon footprints. By lowering urban temperatures, the technology mitigates heat-related energy demands, indirectly cutting greenhouse emissions. Sustainable materials in newer models, such as biodegradable tubing, align with circular economy principles. As climate challenges intensify, nano-misting offers a scalable tool to enhance resilience without depleting resources.